Condens. Matter 2023, 8, 93
Authors: Alina M. Ionescu, Ion Ivan, Corneliu F. Miclea, Daniel N. Crisan, Armando Galluzzi, Massimiliano Polichetti and Adrian Crisan
Abstract: Among various “families” of iron-based superconductors, the quite recently discovered
AeAFe4As4 (where Ae is an alkali-earth metal and A is an alkali metal) has high critical current density,
a very high upper critical field, and a low anisotropy, and has recently received much interest for
the possibility of high magnetic field applications at the liquid hydrogen temperature. We have
performed DC magnetization relaxation and frequency-dependent AC susceptibility measurements
on high-quality single crystals of CaKFe4As4 with the aim of determining the pinning potential
U. The temperature dependence of U displays a clear crossover between elastic creep and plastic
creep. At temperatures around 27–28 K, U* has a very high value, up to 1200 K, resulting in an infinitesimally small probability of thermally activated flux jumps. From the dependence of the
normalized pinning potential on irreversible magnetization, we have determined the creep exponents
in the two creep regimes, which are in complete agreement with theoretical models. The estimation
of the pinning potential from multifrequency AC susceptibility measurements was possible only near
the critical temperature due to equipment limitations, and the resulting value is very close to the one
that resulted from the magnetization relaxation data. Magnetic hysteresis loops revealed a second
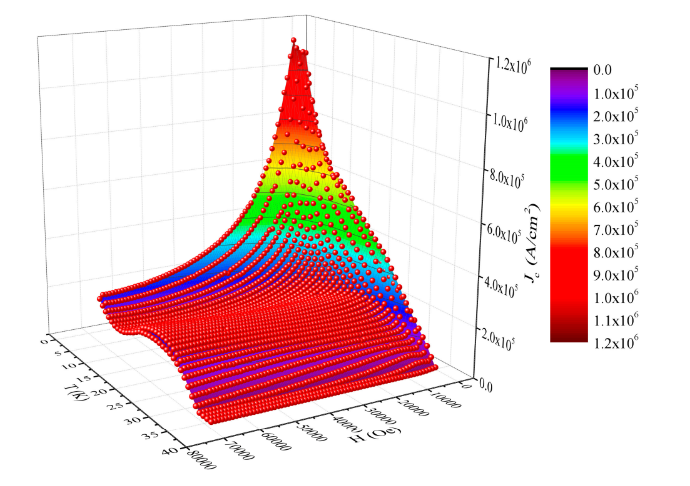
magnetization peak and very high values of the critical current density.